抗体職人のモノクローナル抗体作製サービスは、動物に依存しない独自の抗体作製技術(HuCAL®テクノロジー)により、抗原を高い自由度で設定できるため、抗原のわずかな違いを認識する抗体、あるいは抗原への結合部位を絞り込んだ抗体等、目的に合致した特殊な特異性を持つ抗体も作製いたします。 HuCAL®テクノロジーは、全世界で10年以上の実績があり、14,000もの抗体を作製しております。ここ3年間の成功率は90%以上を誇り、多くの製薬企業等で採用されています。
モノクローナル抗体作製例(作業概要付き)
相同領域に結合する抗体
相同性のあるタンパク質を両方ともご提供頂ければ、どちらのタンパク質も認識する抗体を作製いたします(alternate screening strategy)。2つの異なるアイソフォームを持つタンパク質の両方を認識する抗体が必要な場合やマウスとヒト両由来のタンパク質を認識する抗体が必要な場合におすすめです。
リン酸化修飾を見分ける抗体
リン酸化で修飾されたエピトープのみに結合する抗体を作製することが可能です。セレクションを行う際に、リン酸化の修飾を受けていないペプチドを過剰量で前処理することで、ライブラリから非リン酸化抗原に結合するFab抗体を予め取り除きます。
末端の数アミノ酸を見分ける抗体
N末端(あるいはC末端)の数アミノ酸しか違いがない2種類のタンパク質の内、数アミノ酸が欠損したタンパク質のみを識別する抗体が欲しい場合も、ペプチド抗原を用いて作製することが可能です。例えば、10アミノ酸のペプチド抗原と、2アミノ酸を欠いた8アミノ酸のペプチド抗原を用意し、この抗原の差し引きでパニングを行います(subtraction strategy)。
その他の抗体作製例
Figure 1: ELISA QC of a Phospho-specific Antibody
Phospho-specific antibodies were generated against a 9 amino acid peptide phosphorylated at ser-6 (P-Peptide X1). The library was pre-blocked with the non-phosphorylated peptide and then panned against the phosphorylated peptide coupled to BSA and Transferrin. ELISA QC shows that the antibody specifically recognizes the phosphorylated peptide and does not react with either the non-phosphorylated peptide, an unrelated phosphorylated peptide, or the carrier proteins. Antibody generation took 8 weeks.
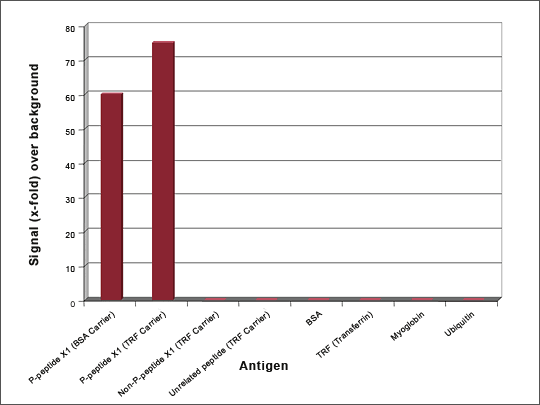
Figure 2: ELISA QC of an Oxidation-specific Antibody
Antibodies were generated against oxidized DJ-1 protein using a 12 amino acid DJ-1 peptide containing the C106 oxidation site. The library was pre-blocked with the non-oxidized peptide (DJ-2 peptide) and then panned against the oxidized DJ-1 peptide coupled to BSA and Transferrin. ELISA QC shows that all 3 selected antibodies specifically recognize the oxidized peptide and do not react with the non-oxidized peptide or the carrier proteins. Antibody generation took 8 weeks. Antibody AbyD3055 was subsequently shown to bind to full length oxidized DJ-1 (Ooe et al., Neurosci Lett. 2006 Oct 9; 406(3); 165-8.)
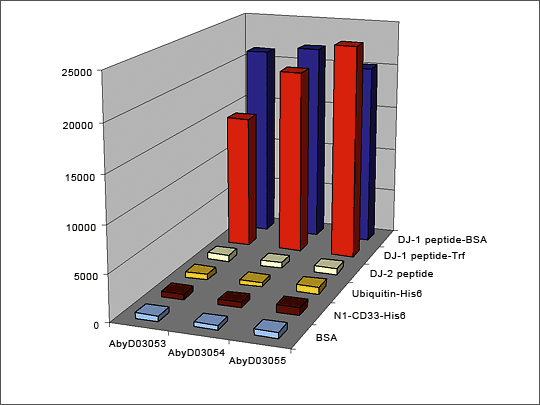
Figure 3: ELISA QC of a Single amino acid mutation-specific Antibody
Antibodies were generated against an x amino acid peptide with a single amino acid mutation at position x. The library was pre-blocked with the wild-type peptide and then panned against the peptide with the single amino acid mutation coupled to both BSA and Transferrin. ELISA QC shows that two of the three antibodies developed specifically recognize the mutant peptide and do not react with either the wild type peptide, or the carrier proteins. The third antibody recognizes both wild-type and mutant peptides. Antibody generation took 8 weeks.
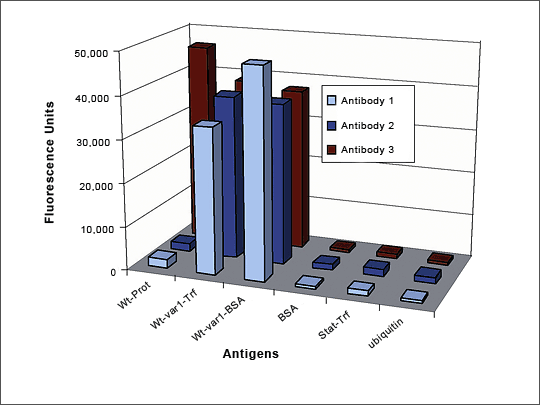
Figure 4: HuCAL Antibody Distinguishes between 8 and 10 aa Peptides
The Fab antibody was generated against the 10 aa peptide. The library was subtracted with the 8 aa peptide coupled to BSA and then panned against the 10 aa peptide coupled to BSA and Transferrin. The HuCAL Fab clearly distinguishes between 10aa peptide and 8aa peptide (difference: lack of 2aa at the N-terminus). Antibody generation time was 8 weeks.
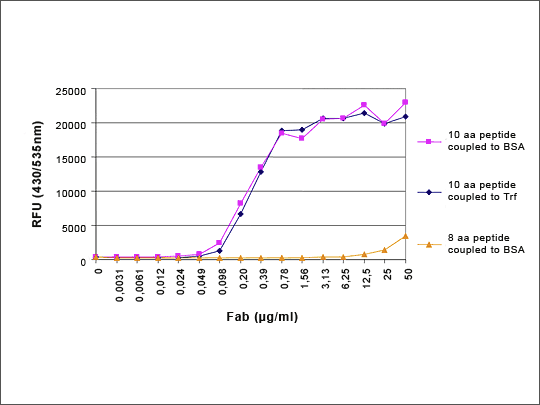
Figure 5: Direct Selection of a Sequence- and Phosphorylation-specific Antibody
Unwanted antibody specificities were first removed by preadsorbing the HuCAL library with related peptides which were either not-phosphorylated (Peptides B and D), or phosphorylated at the same amino acid but with an alternate flanking sequence (Peptide C). The depleted library was then screened against Peptide A to generate phospho- and sequence-specific antibodies. The target peptide was conjugated to both transferrin and BSA carriers for screening, to eliminate carrier specific antibodies. Three antibodies recognizing only the phosphorylated Peptide A were isolated and checked by ELISA.
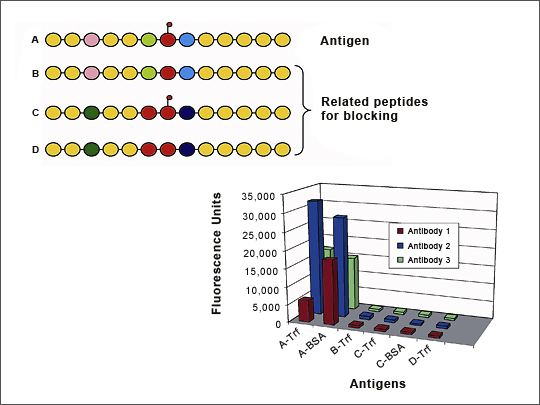
Figure 6: Cross-reactivity Screening After Panning Against Peptide Derived from Mac-1 (CD11b)
The M18 peptide was panned against the HuCAL library and 11 binders were expressed as Bivalent Mini-Antibodies. ELISA QC shows that all 11 antibodies bind specifically to the M18 peptide but not to the BSA or Transferrin carrier proteins, or to an unrelated peptide bound to Transferrin. The I-domain of the parental Mac1 protein is also recognized by 8 of the 11 antibodies.
Figure 7: FACS – Homologous Antigens
Antibodies 1 and 2 were generated against a human protein which has a highly homologous mouse counterpart. FACS analysis of CHO cells expressing both the human and mouse proteins shows that Antibody 1 recognizes both the human and the mouse proteins, while Antibody 2 recognizes only the human form. (Data kindly provided by an academic researcher wishing to remain anonymous.)
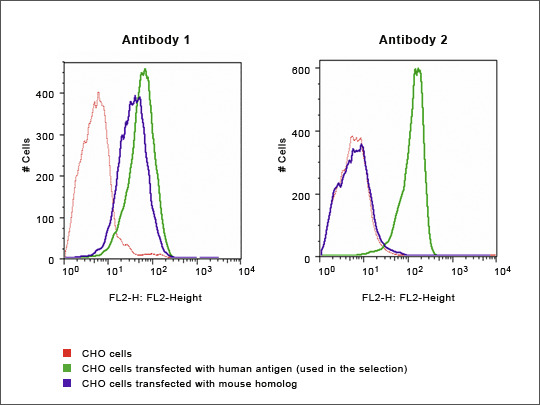
Figure 8: Specificity Profiling on 96 Antigen Microarray
Anti-Cyclophilin A HuCAL-antibody tested on 96 antigens (spotted on micro array). Data kindly provided by Protagen, Germany
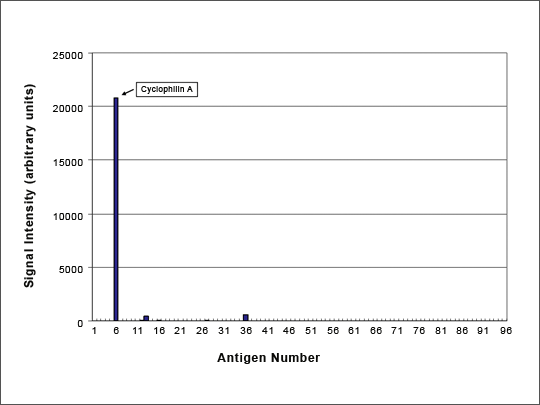
Figure 9: IHC with HuCAL Bivalent Fab Antibody
The HuCAL AgX system was used to generate an MHCII antigen from a cDNA fragment. This antigen was used to pan the HuCAL library for anti-MHCII antibodies. Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human tonsil tissue was treated with a bivalent Fab antibody against MHCII, which was detected using mouse anti-His antibody for bridging and subsequent biotinylated anti mouse – ABC-DAB-detection system. (Data kindly provided by Prof. H. Merz, University of Lübeck, Germany).
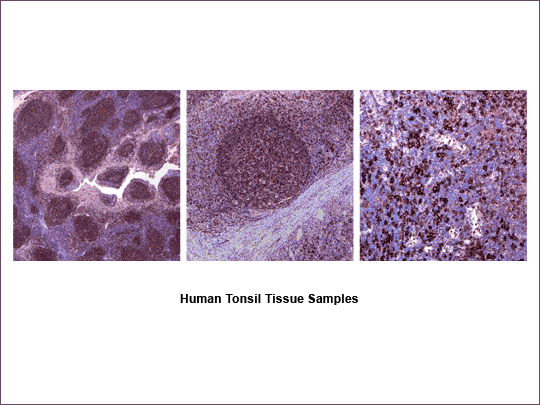
Figure 10: Antibody Specificity – Western Blot
Western blot of mouse tissues and cell lines using a HuCAL Fab generated against an EST-fragment of mKIAA0232. Data courtesy of Dr. O. Ohara, Kazusa DNA Research Institute, Kisarazu, Japan


